The HTTP 400 Bad Request error in Outlook prevents email functionality when the server rejects malformed requests. This guide provides tested solutions for both Outlook Desktop and Web App (OWA), updated for 2025.
What is HTTP 400 Error in Outlook?
The HTTP 400 Bad Request error appears when your Outlook client (desktop or web) sends a request that the server deems invalid or corrupted. It can prevent you from:
- Sending or receiving emails
- Accessing Outlook Web (OWA)
- Syncing mail, calendar, or contacts
- Logging into Outlook through your browser
This issue can stem from either local-side glitches or server-side miscommunication, but in most cases, you can fix it with a few quick steps.
Quick Fixes (Try These First!)
1. Clear Browser/Outlook Cache
Corrupted cache often triggers HTTP 400 errors.
For Outlook Web (OWA) Users:
- Chrome/Edge: Press
Ctrl+Shift+Del→ Select Cached images/files + Cookies → Clear. - Firefox:
Settings → Privacy & Security → Clear Data.
For Outlook Desktop:
- Close Outlook.
- Open Run (
Win + R), type:
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook\RoamCache - Delete all files in the folder.
- Restart Outlook.
Why it works: Removes corrupted temporary files that interfere with server requests.
2. Flush DNS & Use Cloudflare DNS (If Network Issue)
Outdated DNS records can block Outlook from reaching Microsoft servers.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt (Admin) → Run:
ipconfig /flushdns - Optional (if standard DNS fails):
- Go to Control Panel → Network Settings → IPv4 Properties.
- Set DNS to:
- Preferred:
1.1.1.1(Cloudflare) - Alternate:
1.0.0.1
- Preferred:
- Restart your PC.
Note: Avoid this on corporate networks (IT may enforce custom DNS).
3. Repair Outlook Installation
Corrupted Office files can cause HTTP 400 errors.
Steps:
- Go to Settings → Apps → Installed Apps.
- Select Microsoft 365 → Modify → Repair (choose Online Repair for deep fixes).
- Restart your PC.
4. Disable Add-ins/Extensions
Conflicting plugins (especially security tools) may break Outlook requests.
For Outlook Desktop:
File → Options → Add-ins → Manage COM Add-ins → Disable all.- Re-enable one by one to find the culprit.
For Browser (OWA):
- Disable extensions (ad blockers, cookie managers).
- Test in Incognito Mode (Chrome) or Private Window (Firefox).
5. Check OWA Permissions (For Shared/Corporate Mailboxes)
If accessing a shared mailbox fails, ensure Outlook Web is enabled.
For Office 365 Admins:
- Go to Microsoft 365 Admin Center.
- Navigate to Users → Active Users → Select User → Mail Tab.
- Under Email Apps, verify Outlook on the web is enabled.
For Exchange Server 2010: Install Update Rollup 7 (KB2961522) to fix /owa/oma bugs.
Advanced Solutions (For Persistent Errors)
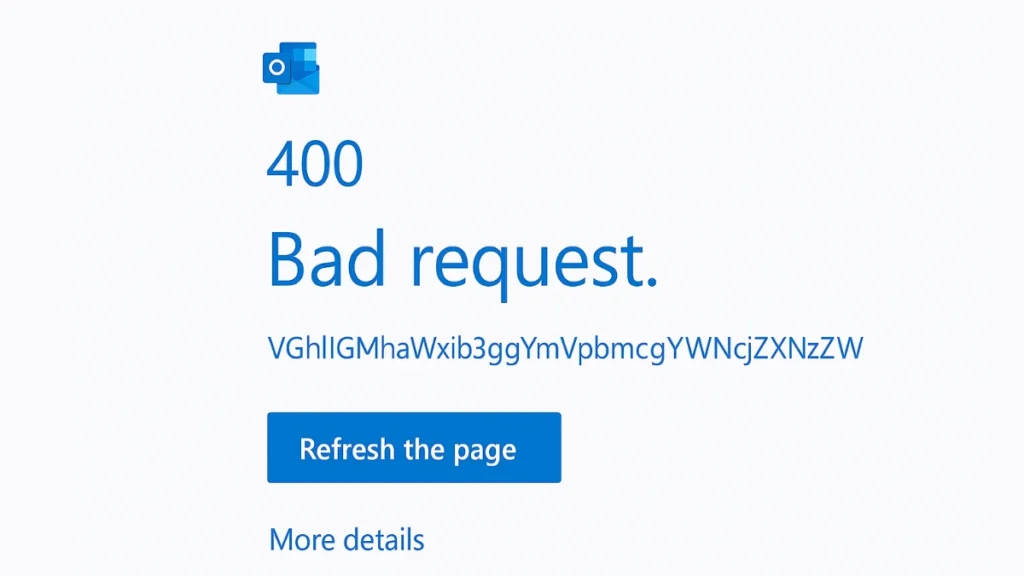
1. Fix Base64-Encoded Errors
If you see an error like:
VGhlIG1haWxib3ggYmVpbmcgYWNjZXNzZWQgZG9lc24mIzM5O3QgaGF2ZSBhIHZhbGlkIGFjY291bnQgc3RhdGUgKCYjMzk7UHJvdG9jb2xEaXNhYmxlZCYjMzk7KS4= Solution:
- Your account may be locked or protocols disabled.
- Contact IT admin or Microsoft Support.
2. Modify Registry (For Exchange Server Errors)
If you’re on Exchange Server and get HTTP 400 due to oversized headers:
- Open Registry Editor (
regedit). - Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HTTP\Parameters - Create/modify these DWORD values:
MaxFieldLength=65534(Decimal)MaxRequestBytes=65534(Decimal)
- Restart the server.
Warning: Only for IT admins—incorrect edits can destabilize systems.
3. Reduce Attachment Sizes
Outlook may reject emails with large attachments (>20MB).
Fix:
- Compress files (ZIP/RAR).
- Upload to OneDrive/ Google Drive and share links.
Emergency Workarounds
If nothing works:
- Try a different browser (Edge/Firefox instead of Chrome).
- Use Outlook Mobile App as a temporary solution.
- Restart your router/PC to reset network glitches.
Corporate User? Check These!
If you’re in an enterprise environment, your IT team might:
- Block OWA in Exchange Admin Center.
- Enforce firewall/ proxy rules blocking Outlook traffic.
- Restrict custom DNS (like Cloudflare).
Ask IT to verify:
- Exchange Admin Center → Mailbox → Email Apps (enable OWA).
- No HTTP packet size limits on servers.
Final Thoughts
This updated guide merges proven fixes with real-world insights from user reports. Most HTTP 400 errors are resolved via cache clearing, DNS fixes, or OWA settings. For stubborn cases, registry edits or IT support may be needed.
Did this work? Let us know which solution helped you!